Authentication System
Overview
The authentication system provides user registration, login, and session management functionality for the web application.
Login System
The login system allows registered users to authenticate and access their accounts.
Login Mechanism Flowchart
Authentication Steps
Initial Access
- User navigates to login page
- System checks for existing session
- If session exists, redirect to dashboard
Credential Input
- User enters email/username
- User enters password
- Form includes CSRF token for security
Input Validation
- Sanitize user input
- Validate email format
- Check required fields
- Verify CSRF token
Database Verification
php$stmt = $conn->prepare("SELECT * FROM users WHERE email = ?"); $stmt->bind_param("s", $email); $stmt->execute();Password Verification
phpif (password_verify($password, $user['password'])) { // Password is correct }Session Management
phpsession_start(); $_SESSION['user_id'] = $user['id']; $_SESSION['username'] = $user['username']; $_SESSION['role'] = $user['role'];Access Control
- Redirect to appropriate dashboard
- Set session timeout
- Record login timestamp
Features
- Secure password handling
- Session management
- Remember me functionality
- Error handling and user feedback
Error Handling
- Invalid credentials notification
- Account status checking
- Brute force protection
Registration System
The registration system allows new users to create accounts.
Features
- Email validation
- Password strength requirements
- Duplicate account checking
- Account activation process
Registration Process
- Navigate to the registration page
- Fill in required information:
- Username
- Password
- Confirm Password
- Accept terms and conditions
- Submit registration form
Validation Rules
- Username: Alphanumeric, 3-20 characters
- Email: Valid email format
- Password: Minimum 8 characters, including:
- At least one uppercase letter
- At least one lowercase letter
- At least one number
- At least one special character
Security Considerations
- Passwords are hashed using modern algorithms
- CSRF protection implemented
- Rate limiting on login attempts
- Secure session handling
- SQL injection prevention
Session Security
php
// Session configuration
ini_set('session.cookie_httponly', 1);
ini_set('session.use_only_cookies', 1);
ini_set('session.cookie_secure', 1);
// Session regeneration
session_regenerate_id(true);Brute Force Prevention
php
// Login attempt tracking
if ($failed_attempts >= 3) {
// Implement temporary lockout
// Record IP address
// Send security alert
}Error Messages
- "Invalid email or password"
- "Account is locked"
- "Too many login attempts"
- "Session expired"
Success Flow
- Valid credentials submitted
- Session created
- User data loaded
- Redirect to dashboard
Failure Flow
- Invalid credentials
- Error message displayed
- Login form preserved
- Attempt counted
Related Components
- User registration system
- Password reset functionality
- Session management
- Security monitoring
Login Implementation Details
The login system is implemented in login.php and follows secure authentication practices. Here's a detailed breakdown of the implementation:
Session Management
php
session_start();
if (isset($_SESSION['username'])) {
header("Location: admin/index.php");
exit;
}- Initializes PHP session at the start
- Checks if user is already logged in
- Redirects authenticated users to admin dashboard
Database Connection
php
require_once "admin/config.php";- Includes database configuration file
- Establishes secure database connection
Authentication Process
1. Form Submission Handling
php
if ($_SERVER["REQUEST_METHOD"] == "POST") {
$username = $_POST['username'];
$password = $_POST['password'];- Validates that request is POST method
- Captures username and password from form submission
2. User Verification
php
$stmt = $conn->prepare("SELECT * FROM users WHERE username = ?");
$stmt->bind_param("s", $username);
$stmt->execute();
$result = $stmt->get_result();- Uses prepared statements to prevent SQL injection
- Securely queries database for user
- Binds username parameter to prevent SQL injection
3. Password Verification
php
if ($result->num_rows == 1) {
$row = $result->fetch_assoc();
if (password_verify($password, $row['password'])) {
$_SESSION['username'] = $username;
$_SESSION['role'] = $row['role'];
header("Location: admin/index.php");
exit;
}
}- Checks if user exists
- Verifies password using secure
password_verify()function - Sets session variables upon successful login
- Stores user role for access control
- Redirects to admin dashboard
Error Handling
php
} else {
$error_message = "Incorrect password";
}
} else {
$error_message = "User not found";
}- Provides specific error messages for:
- Incorrect password
- Non-existent user
- Maintains security by not revealing which specific credential was incorrect
Security Features
SQL Injection Prevention
- Uses prepared statements
- Parameters are properly bound
- Input is sanitized
Password Security
- Passwords are hashed (not stored in plain text)
- Uses PHP's secure
password_verify()function - Implements server-side validation
Session Security
- Sessions are properly initialized
- Session variables are securely managed
- Implements proper session termination
XSS Prevention
- Error messages are properly escaped:
phphtmlspecialchars($error_message, ENT_QUOTES, 'UTF-8')
User Interface
The login form includes:
- Username input field
- Password input field
- Error message display
- Registration link for new users
- Clean and responsive design using CSS
Login Interface
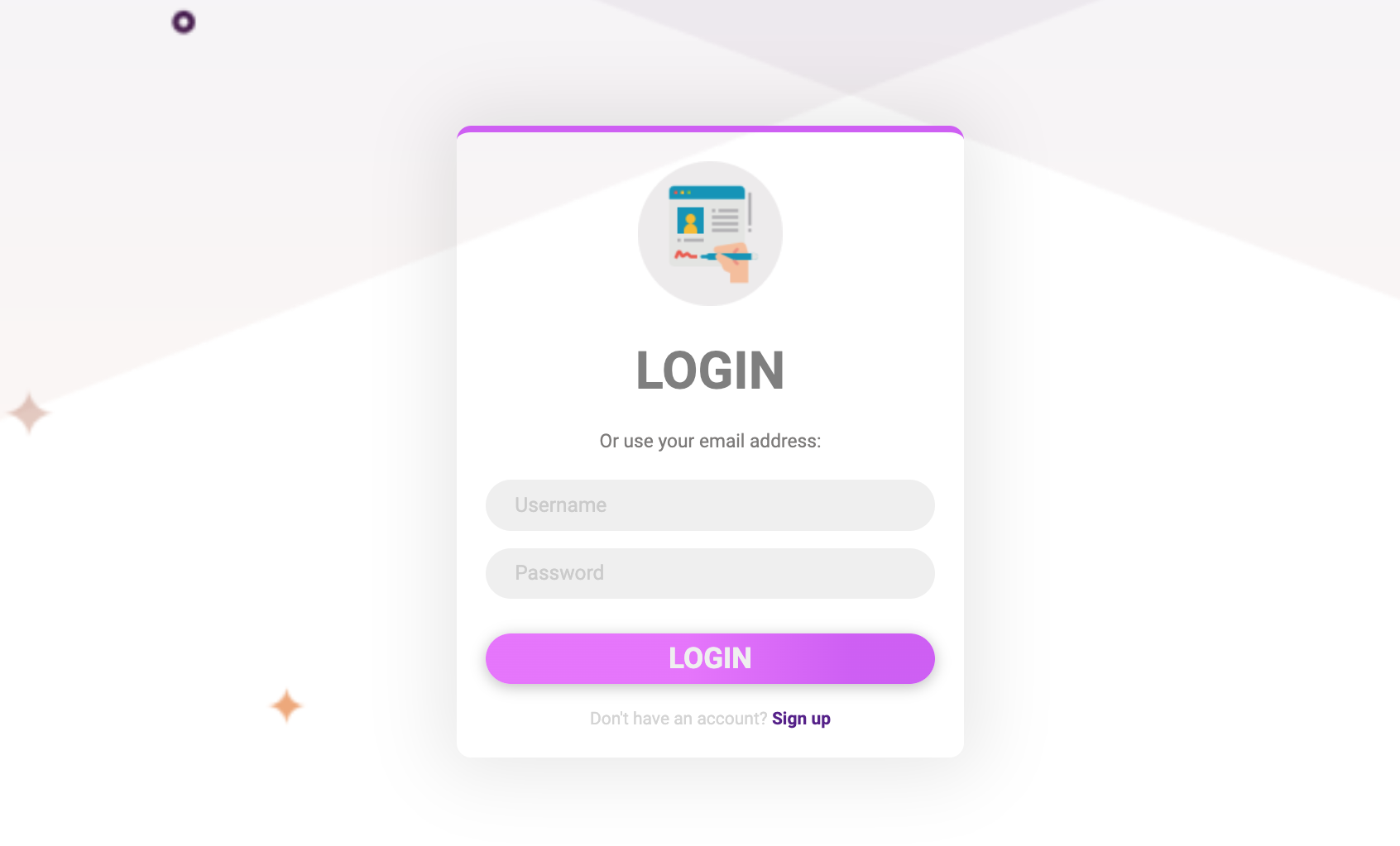 The login interface with email/username and password fields
The login interface with email/username and password fields